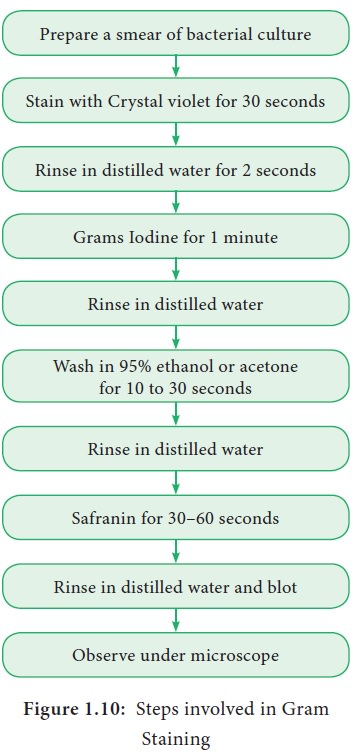
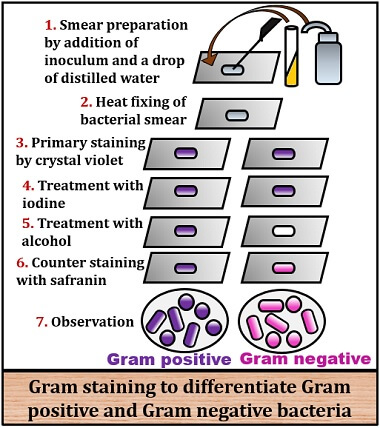
Describe What Happens at Each Step in the Gram Stain
The various steps involved in Grams staining are detailed below. Crystal violet is primary stain leave on for 1 min 3.
Gram Staining Procedure Bacteria
The stained smear is rinsed again and then a decolorizing agent is added to removed the dye-mordant complex from the.
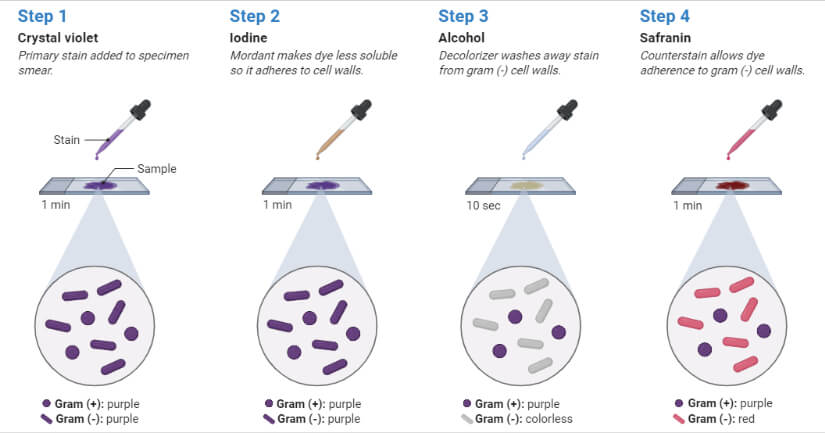
. Steps of Gram stain. 1 Crystal violet is the primary stain entering the cytoplasm and imparting a color to all cells that can be stained. The procedure is based on the reaction between peptidoglycan in the cell walls of some bacteria.
It is a basic dye that interacts with negatively charged components of the cell wall and membrane. The gram-staining is a procedure that differentiates bacteria by their cell wall. CV dissociates in aqueous solutions into CV and Cl ions.
Let the stream of water flow slowly along the surface such that only the stain is flooded and the smear is intact. The smear is flooded with the primary stain. Please type the answer.
Distinguishes cell wall chemistry either gram or -. Step 1 of 5. Red bc alcohol washed away lipid layer and it absorbed safranin.
Every student and professional who works with bacteria has to at some point learn how to do a Gram stain. Excess stain over the treated sample is. 1 Application of the primary stain Crystal Violet CV to a heat-fixed smear of bacterial culture.
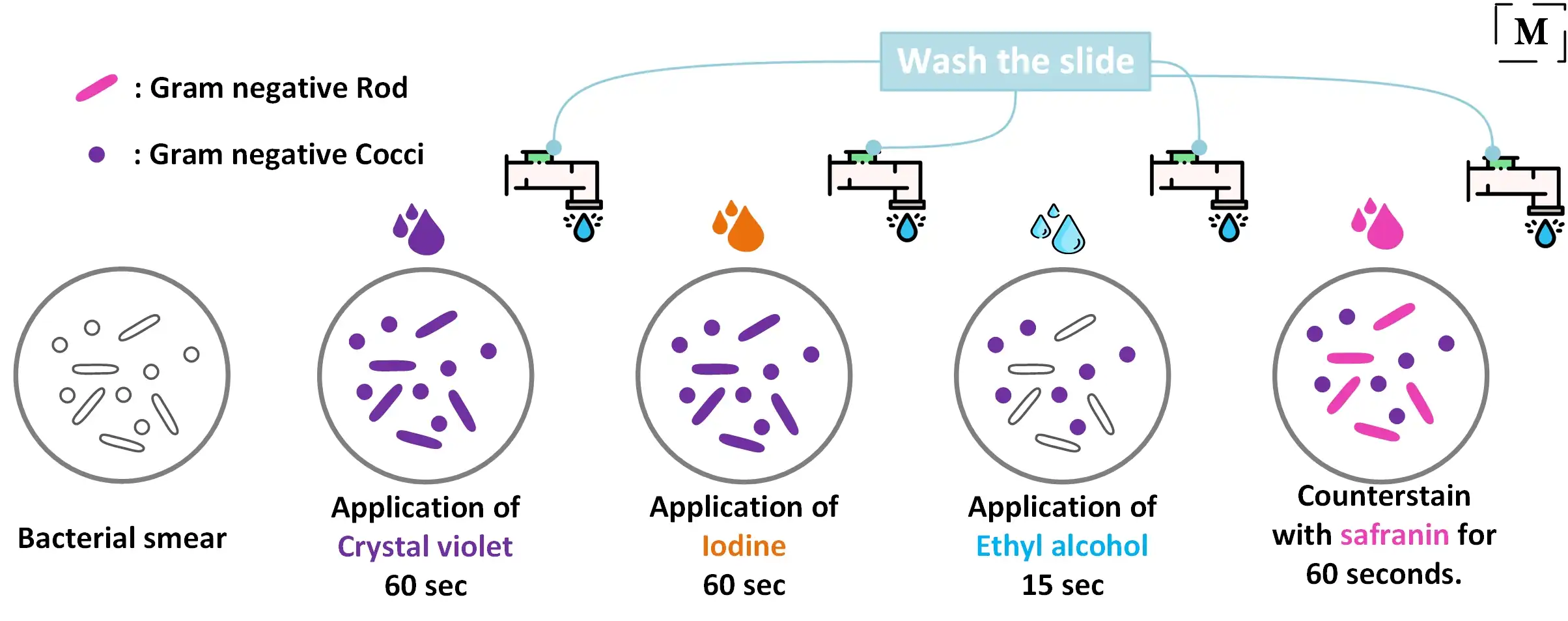
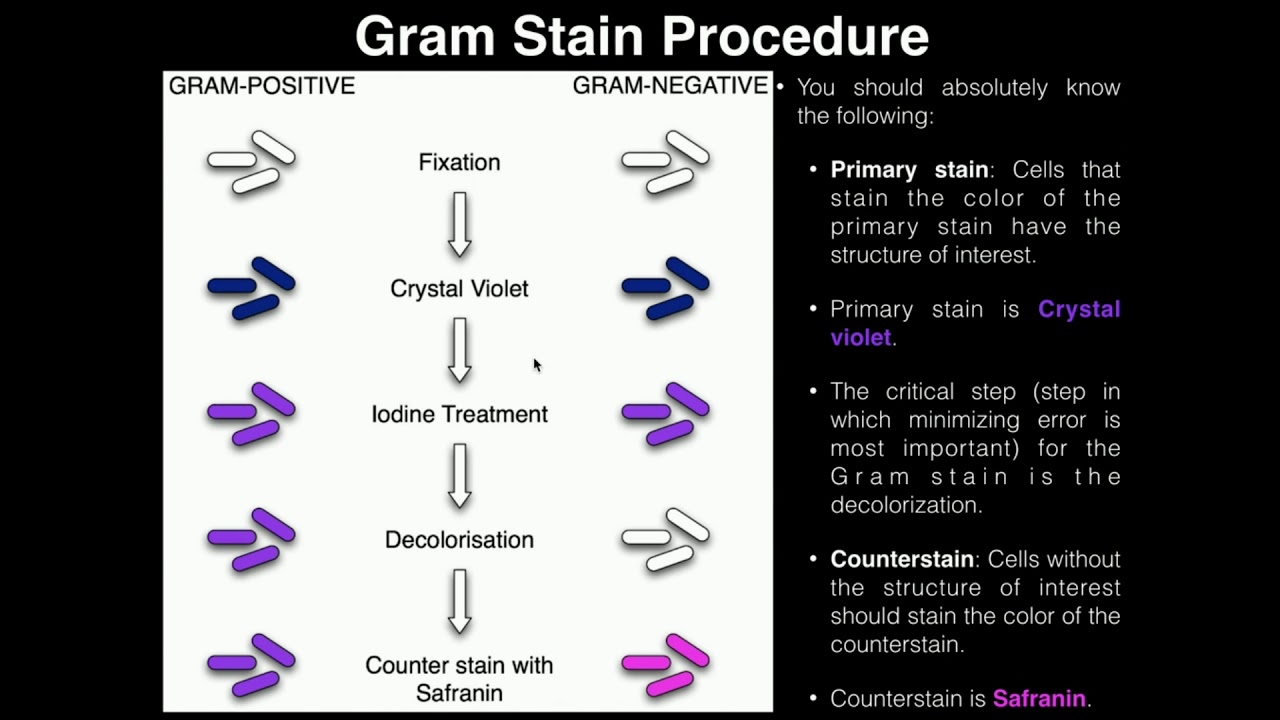
Iodine The mordant binds to the chemical dye helping to hold it so it remains stuck so that alcohol doesnt wash it away. If the bacteria is Gram positive it will retain the primary stain crystal violet and not take the secondary stain safranin causing it to look violetpurple under a microscope. Decolorizing with ethanol 5.
Enter cytoplasm and colors all cells that can be stained 2 Iodine complexes with crystal violet acting as a mordant to enhance affinity of cellular components for dye. Iodine is added and acts as a mordant and causes the crystal violet to form large crystals within the cell wall leave on for 1 min 5. Describe what happens at each step in the Gram stain.
Application of counterstain safranin. If the bacteria is Gram negative it will lose the primary stain and take the secondary stain causing it to appear red when viewed under a microscope. Be sure to mention what color are the cells AND WHY.
Gram- bacteria lose the crystal violet color after decolorizing with alcohol since they lack the peptidoglycan layer. The decolorizing step is the most critical in Gram staining. The Gram stain involves staining bacteria fixing the color with a mordant decolorizing the cells and applying a counterstain.
The outcome in this step is based on how easily the cell releases the crystal violet-iodine complex. The purpose of each step of a gram stain is to stain and decolorize the cells in order to differentiate the organisms in the Domain Bacteria according to their cell wall composition. The Classic Gram Stain.
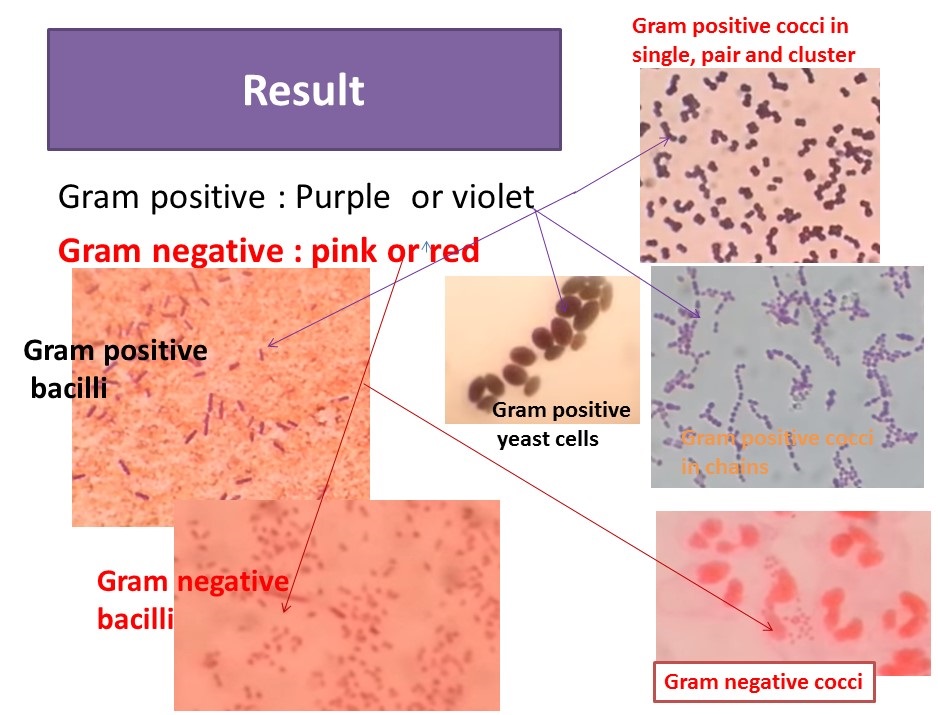
Dividing bacterial cells in two major groups Gram positive and Gram negative it is a. The Gram stain is a staining procedure used to not only make. Purple bc they do not absorb safranin since crystal violet was locked in cell walls.
Hans Christian Gram in 1884 the Gram stain is a differential stain that is used in identifying bacteria. The gram-negative bacteria appear colorless and gram-positive bacteria remain blue. 2 Iodine complexes with the crystal violet within the cell acting as a mordant to enhance the affinity of the cellular components for a dye.
Crystal violet added to the smear. While washing the slide after staining do not let the water stream fall directly on the smear. Find information and process for the Preparation of Gram Staining Regent.
A decolorizer made of acetone and alcohol. Counterstaining with crystal violet. Therefore under a microscope and after the staining procedure Gram bacteria appear violetpurple in colr while Gram appear pink.
Describe what happens in each step of a gram stain 1 Crystal violet is primary stain. How do gram apear. Decolorisation step should not exceed the time limit.
Iodine the mordant this fixes the violet 3. There are majorly 4 steps of a gram stain. The gram-positive bacteria remain blue.
Be very specific about what is happening at each step and why it happens. Describe in detail what happens in each step. The steps in Gram staining are.
The four basic steps of the Gram Stain are. The sample is adhered over the slide and is stained under the aseptic conditions. Safranin is a counter stain since it is picked by the Gram bacteria that have lost the crystal violet dye.
Besides safranin dilute carbol fuchsin solution is also used as a counterstain. Initially the sample is stained with crystal violet dye. Gram-positive bacteria have only one lipid bilayer with a.
Always prefer to observe under 10X first. These two ions then penetrate through the cell wall and cell membrane of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative cells. Primary stain with safranin 3.
Gram-negative bacteria contain two lipid bilayers with a thin layer of peptidoglycan separating the two membranes. The red dye safranin stains the decolorized gram-negative cells redpink. The steps in gram staining involve a series of staining and decolorization.
How do gram - apear. Counter Stain Safranin It is a red-colored counterstain used to stain decolorized Gram-Negative cells in the Gram Staining technique. Both gram-positive and gram-negative cells have.
Make smear according to previous exercise. This may disrupt the smear. What happens when you reverse safranin and crystal violet in gram stain procedure.
The primary stain crystal violet binds to peptidoglycan coloring cells purple. Describe the Gram stain technique and the effect on Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria after each step. The smear is rinsed to remove excess primary stain and then flooded with a mordant.
Gram Staining Better Understanding Of The Procedure And Easy Interpretation Of The Results

Gram Stain Introduction Principle Procedure Result And Interpretation
Gram Staining Principle Reagents Procedure Steps Results
Gram Stain Definition And Patient Education
How Would You Explain The Mechanism Of Gram Staining Quora
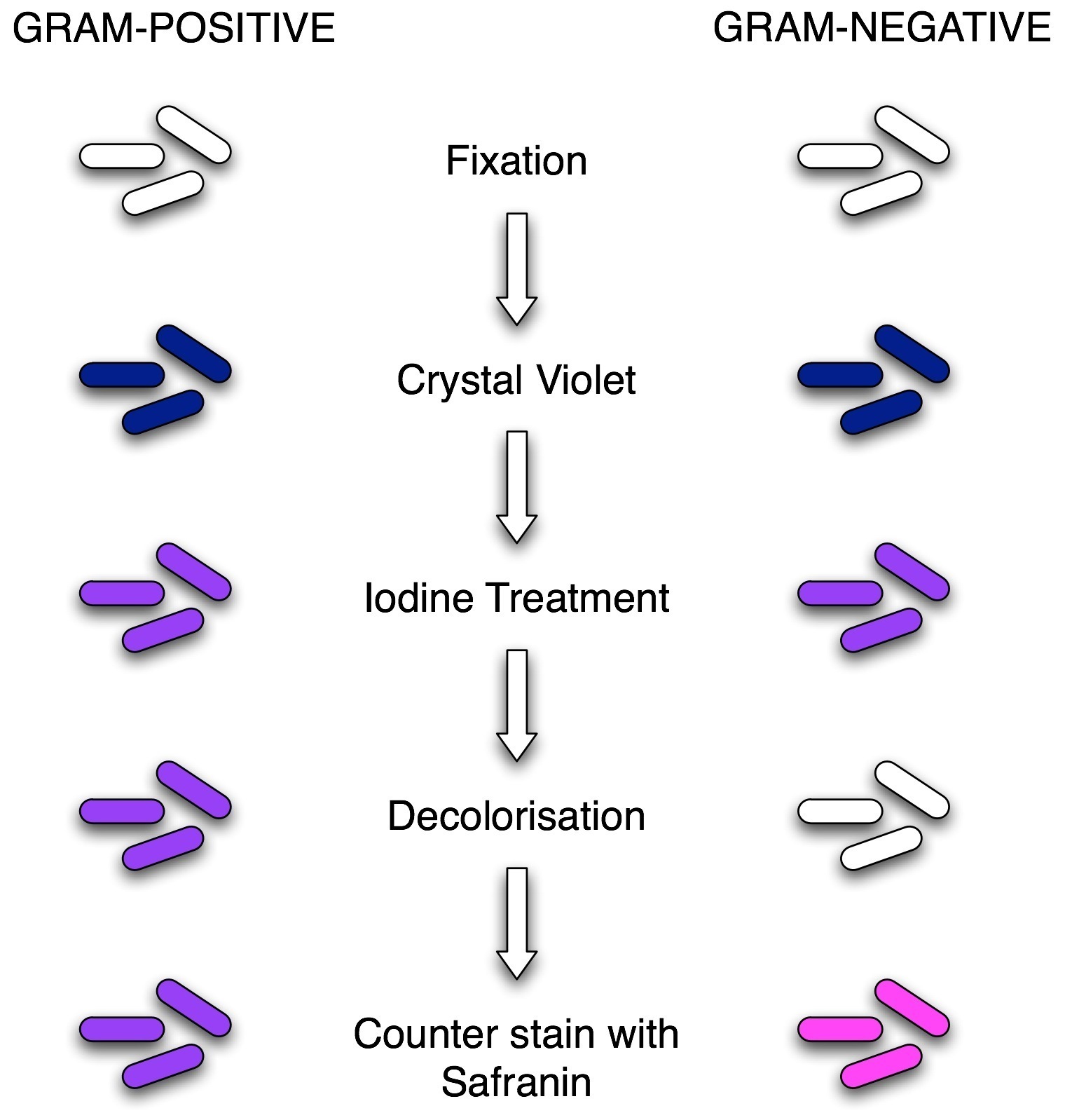
Gram Staining Principle Procedure And Results

Ex 3 Gram Stain Technique Flashcards Quizlet
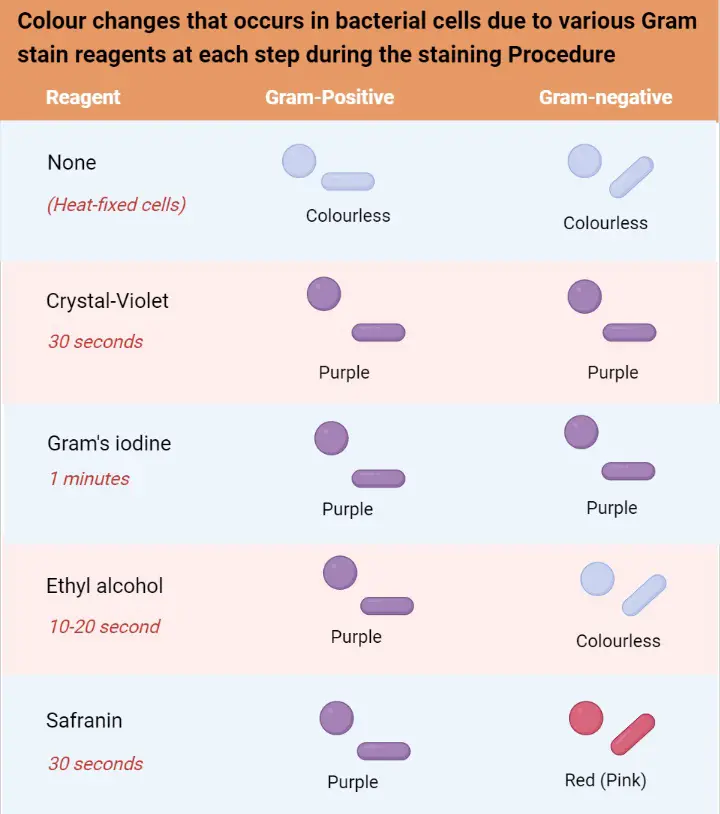
Gram Staining Procedure Principle And Results
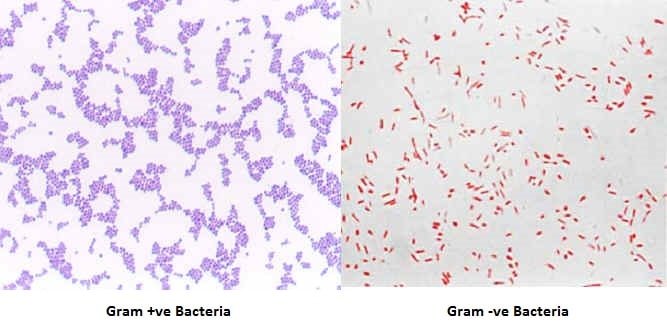
Gram Staining Principle Procedure Interpretation Examples And Animation

Pin On Bacteria Science Experiment Grown On The Plates
What Is Gram Staining Definition Video Principle Process Significance Biology Reader
Lab Exercise 3 Heat Fixing And Gram Staining Youtube
What Purpose Does Gram Staining Serve Quora
How Would You Explain The Mechanism Of Gram Staining Quora


/gram-positive-staphylococcus-aureus-bacteria-541802136-57979cca5f9b58461f26eccc.jpg)

Comments
Post a Comment